RMC
A
C++ implementation of the Reverse Monte Carlo algorithm
|
01.03.2023: NEW, 2023.1
VERSION OF RMC_POT IS AVAILABLE on the download
page!!!
|
What is RMC good for? |
RMC_POT
is a C++ implementation of the Reverse Monte Carlo algorithm for deriving 3D structures of
disordered materials from mainly diffraction data, but additional information
as EXAFS data and different constraints can be used as well. It can be used in
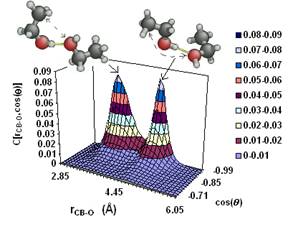
case of a wide range of materials with disordered structures as simple or
molecular liquids, glasses, amorphous materials, nanoparticles
It can
work with periodic boundary condition using a cubic simulation cell, or with
non-periodic boundary conditions for a spherical sample.
If you
have neutron, X-ray or electron diffraction data for disordered materials and
you are interested in their structure, then you can build 3-D structural models
with RMC in good agreement with the experimental data.
|
|
|
|
|
To learn
more about RMC, visit the References page.
RMC code
provided here is not applicable for crystalline materials!
If you have small angle neutron scattering data (SANS),
then visit the RMCSANS
website.
|
How to use RMC_POT |
The
detailed description how to use the code can be found in the RMC_POT user
guide.
If you want to use only basic functionalities, see page Quick start.
|
What's on the RMC++ web site? |
At the moment, you will find
- a short description of the RMC algorithm
- downloads of RMC++ packages for Windows and Linux operating systems (executables and source code)
- description of how to start RMC quickly
- commented examples of applications
- how to customize RMC++ for implementation of molecular moves.
- comments on special topics relevant to the RMC algorithm and RMC++.
- familiarize with different code options
- the full documentation for RMC++
- RMC++ references and links
- the code development history
- How to contact us
Last modified 04/03/2023) by Orsolya Gereben
(comments welcome!)